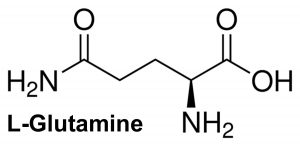
 L-Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the human body, a key building block for protein, and is naturally produced by muscles and transported via the bloodstream to the organs that require it. L-glutamine is abundant in a healthy balanced diet containing plenty of raw, leafy vegetables, beans and legumes, meat and dairy products, however certain periods of life can create a demand for increased L-glutamine intake. This increased intake may be required during or following stress, trauma, major infections, intense exercise, immunotherapy and chronic gastrointestinal disorders, or simply due to a lack of L-glutamine in the diet.
L-Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the human body, a key building block for protein, and is naturally produced by muscles and transported via the bloodstream to the organs that require it. L-glutamine is abundant in a healthy balanced diet containing plenty of raw, leafy vegetables, beans and legumes, meat and dairy products, however certain periods of life can create a demand for increased L-glutamine intake. This increased intake may be required during or following stress, trauma, major infections, intense exercise, immunotherapy and chronic gastrointestinal disorders, or simply due to a lack of L-glutamine in the diet.
L-glutamine supports the normal immune function, intestinal health, muscle recovery and decreases soreness after exercise. By acting as a source of fuel for the intestinal cells, L-glutamine helps maintain healthy barriers of the intestinal lining and overall gut health. This action has led it to be a subject of IBS research for a number of years and shows promising results. L-glutamine is a major fuel source for rapidly dividing cells during healing, has potent antioxidant properties and stimulates immune cell activity, overall supporting a normal immune response to wounds and infection. Protein supplementation has long been used by athletes to encourage muscle recovery and studies indicate that L-glutamine in particular may result in faster recovery from muscle soreness after eccentric exercise. L-Glutamine and intestinal lining L-Glutamine and the immune system L-Glutamine and muscle soreness after eccentric exercise.
Sources

